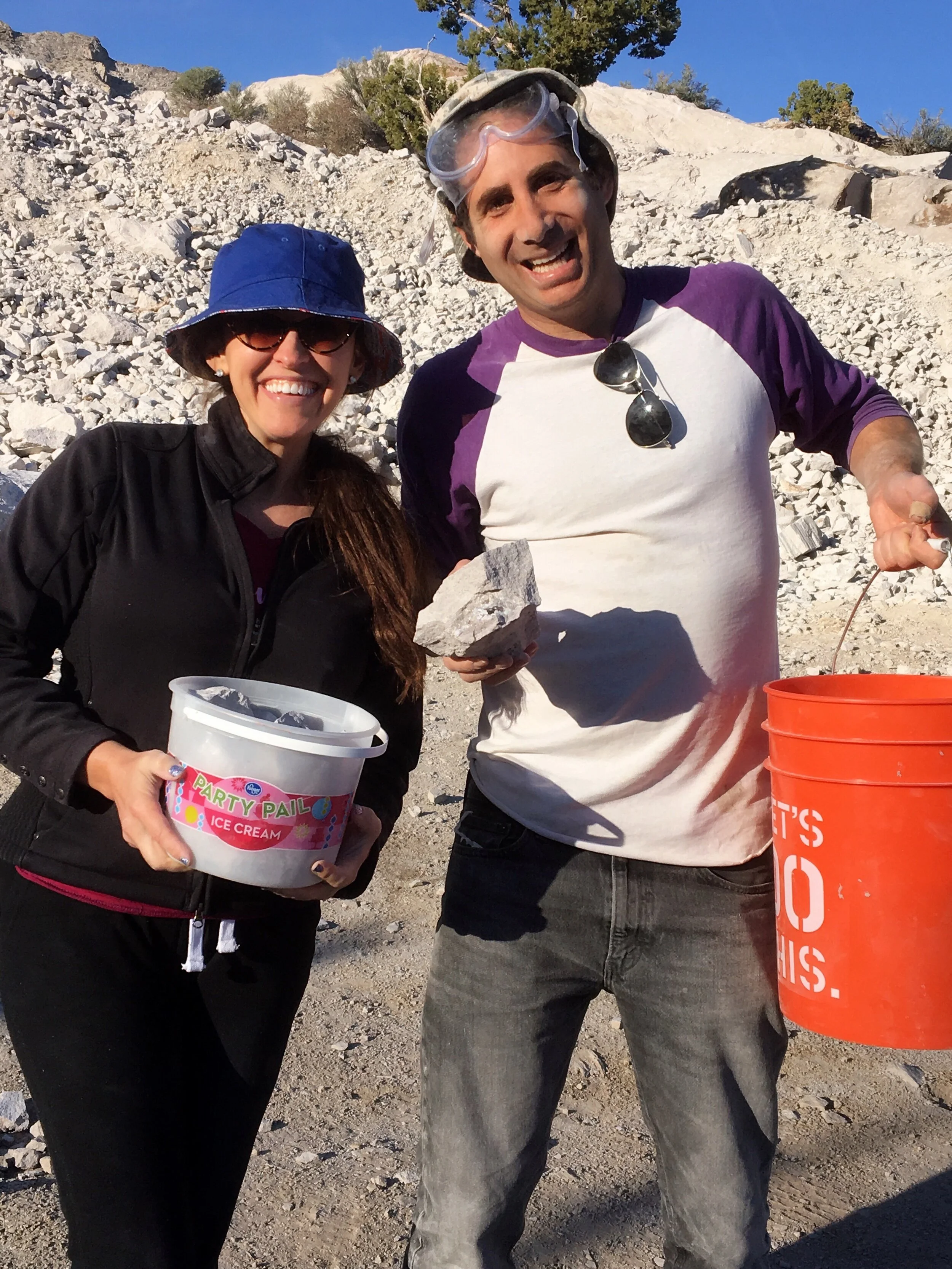
Meet the author Derek Taylor Kent and his wife, author Sheri Fink!
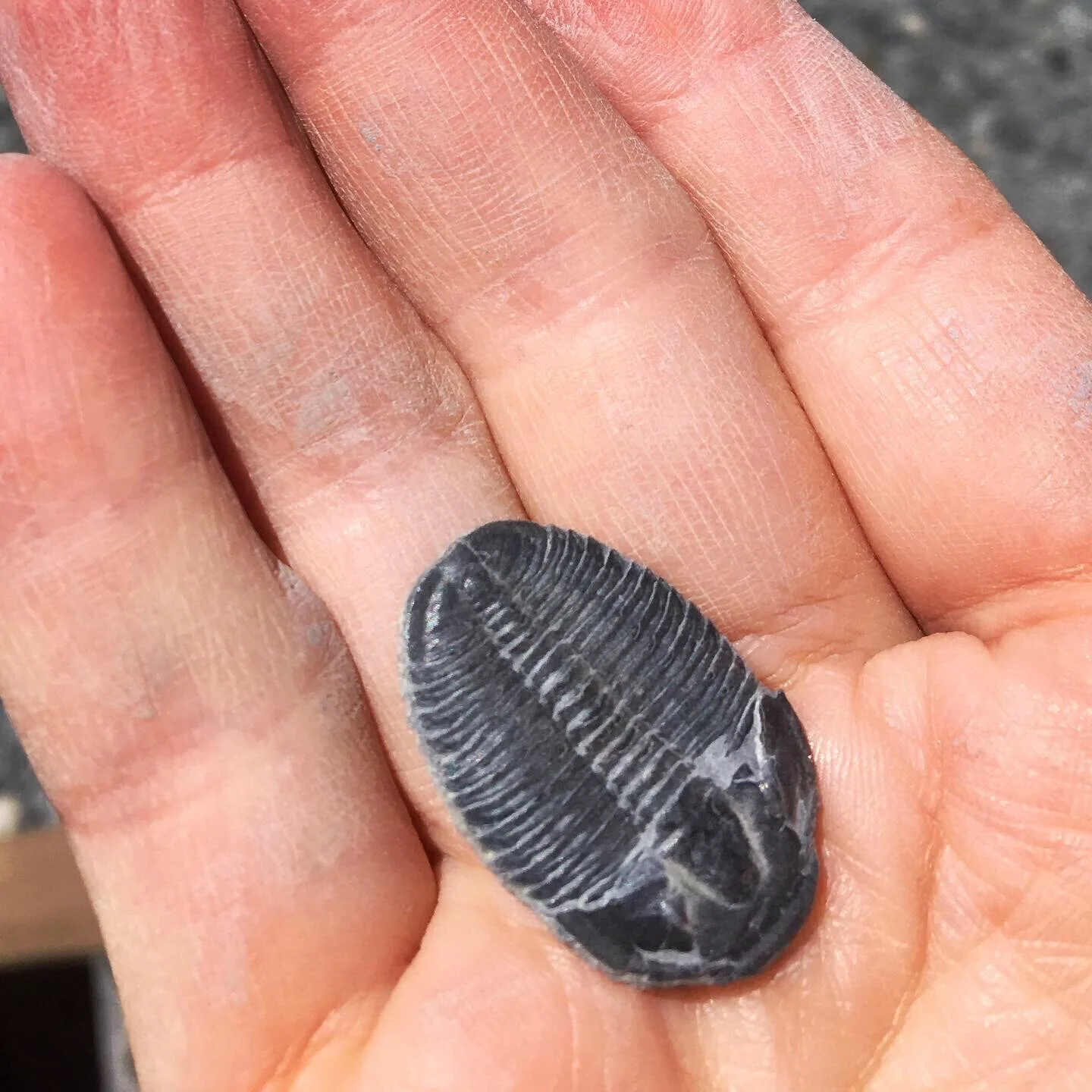
Check out our fossil-hunting adventure below and learn about all the dinosaurs in Dinosaur Derby.
You read the book, now let’s learn more about all those awesome dinosaurs!
Warning: Some dinos bite :)
In the book the Tyrannosaurs Rex rides in a race car, but that would have to be one BIG car! How many people do you think could fit in just one T-Rex-sized car?
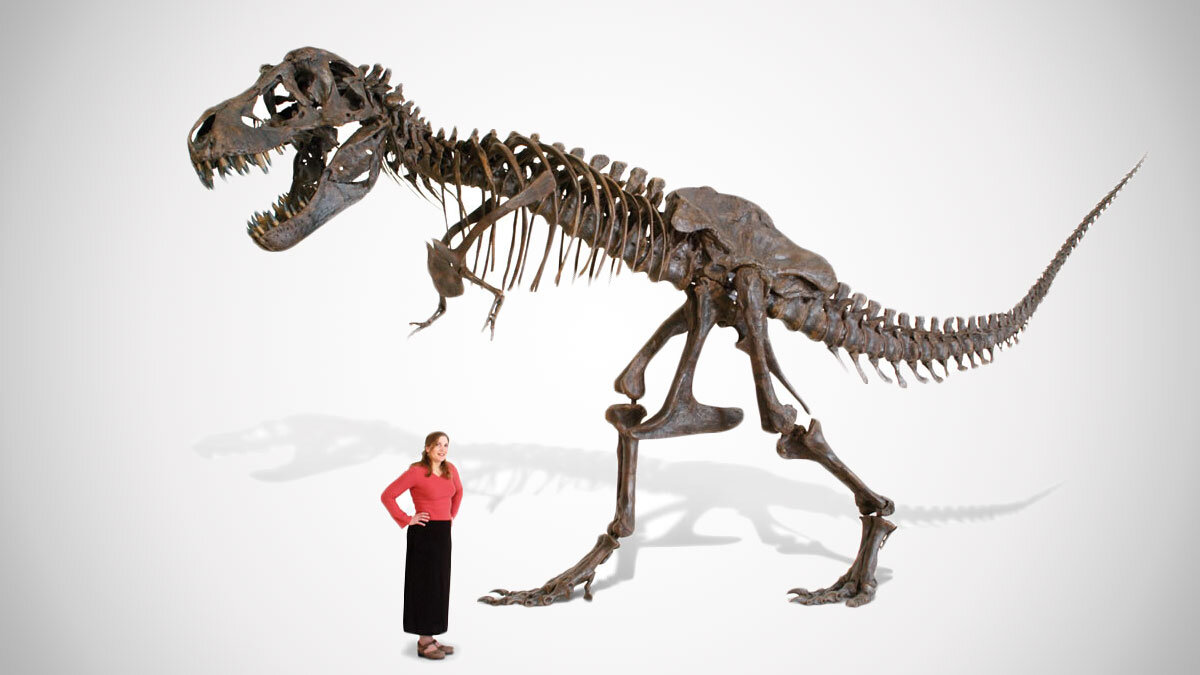
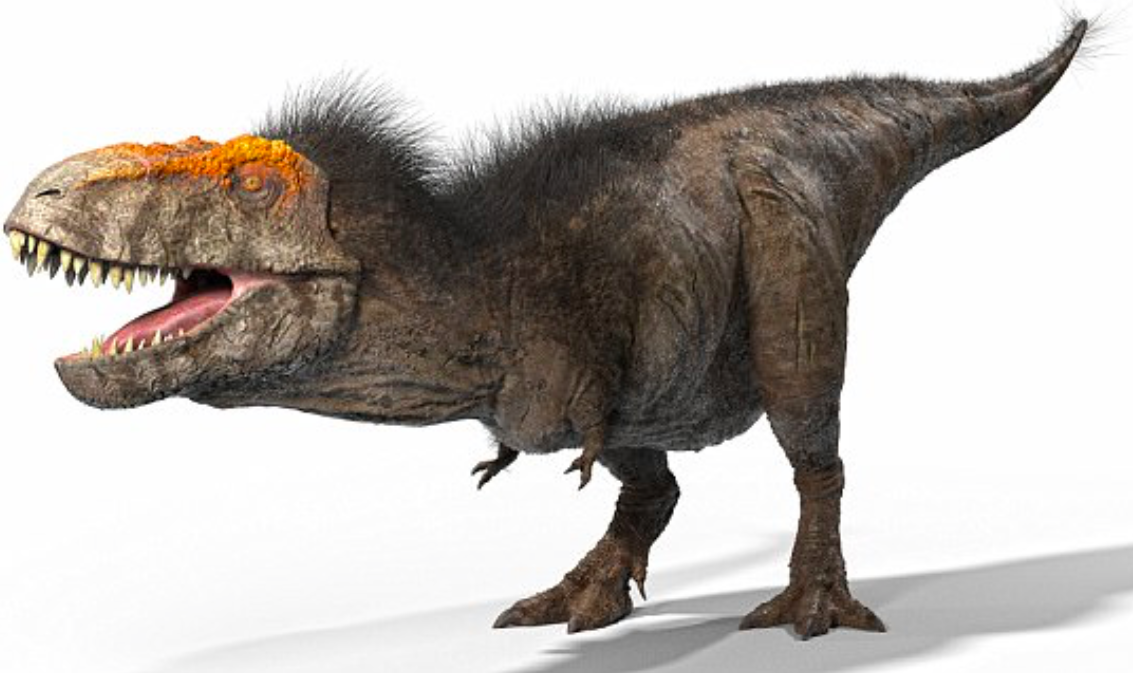
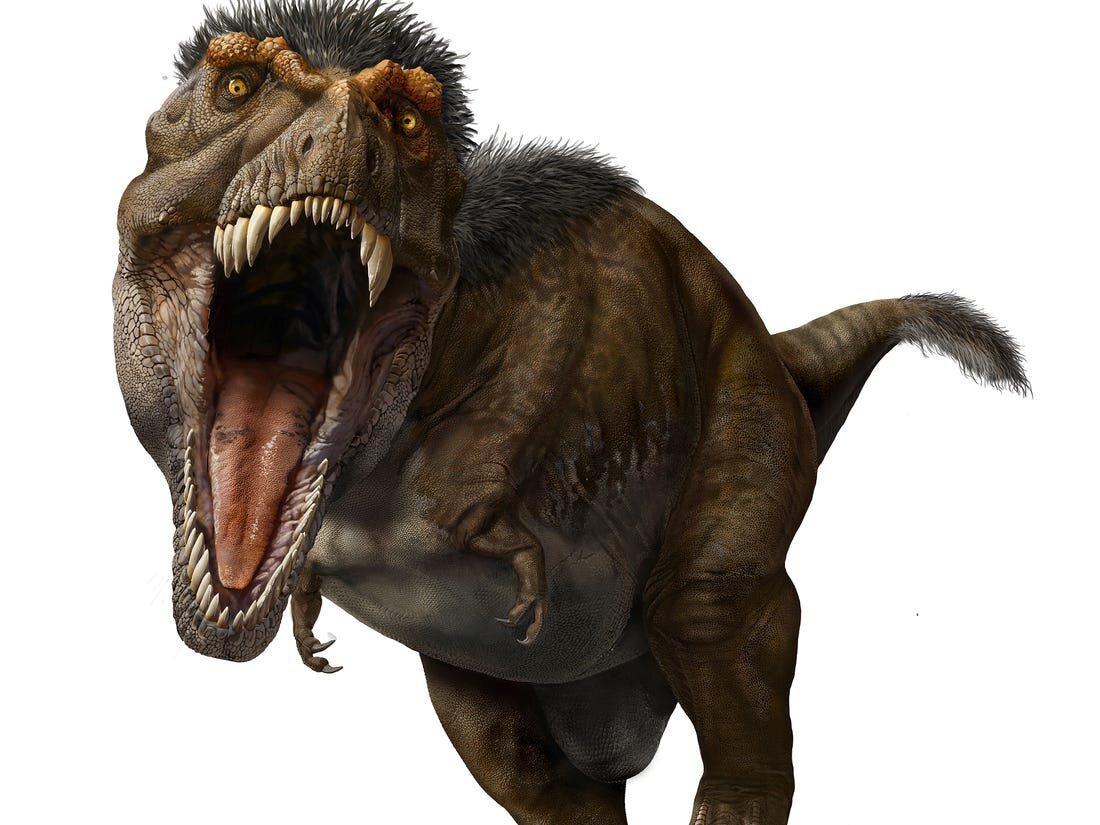
Tyrannosaurus Rex
The species Tyrannosaurus rex (rex meaning "king" in Latin), often called T. rex or colloquially T-Rex, is one of the most well-represented of the large theropods. Tyrannosaurus lived throughout what is now western North America, on what was then an island continent known as Laramidia. Tyrannosaurus had a much wider range than other tyrannosaurids. Fossils are found in a variety of rock formations dating to the Maastrichtian age of the upper Cretaceous Period, 68 to 66 million years ago. It was the last known member of the tyrannosaurids, and among the last non-avian dinosaurs to exist before the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event - AKA the giant meteor that crashed into Earth 65 million years ago.
Like other tyrannosaurids, Tyrannosaurus was a bipedal carnivore with a massive skull balanced by a long, heavy tail. Relative to its large and powerful hind limbs, Tyrannosaurus forelimbs were short but unusually powerful for their size and had two clawed digits. The most complete specimen measures up to 12.3 m (40 ft) in length though T. rex could grow to lengths of over 12.3 m (40 ft), up to 3.66 meters (12 ft) tall at the hips, and according to most modern estimates 8.4 metric tons (9.3 short tons) to 14 metric tons (15.4 short tons) in weight. Although other theropods rivaled or exceeded Tyrannosaurus rex in size, it is still among the largest known land predators and is estimated to have exerted the strongest bite force among all terrestrial animals. By far the largest carnivore in its environment, Tyrannosaurus rex was most likely an apex predator, preying upon hadrosaurs, armored herbivores like ceratopsians and ankylosaurs, and possibly sauropods. Some experts have suggested the dinosaur was primarily a scavenger. The question of whether Tyrannosaurus was an apex predator or a pure scavenger was among the longest debates in paleontology. Most paleontologists today accept that Tyrannosaurus was both an active predator and a scavenger.
As the archetypal theropod, Tyrannosaurus has been one of the best-known dinosaurs since the early 20th century, and has been featured in film, advertising, postal stamps, and many other media.
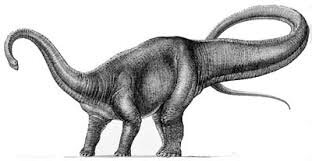
Diplodocus flies in a tiny airplane in Dinosaur Derby, but of course in real life it would have weighed far too much to stay in the air! How big do you think an airplane would have to be to fit an actual Diploodocus inside?
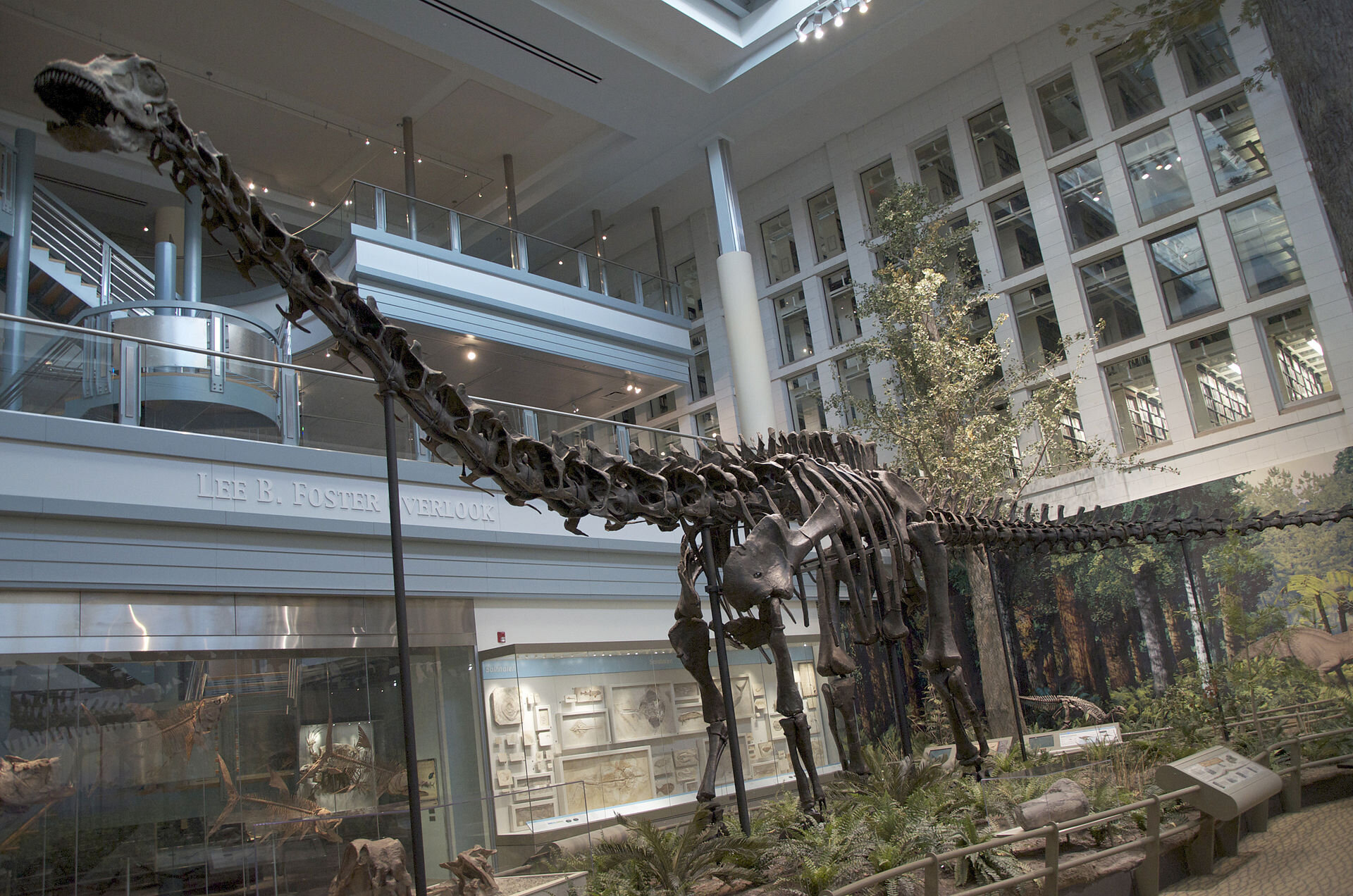
Diplodocus
Diplodocus is a genus of diplodocid sauropod dinosaurs whose fossils were first discovered in 1877 by S. W. Williston. The generic name, coined by Othniel Charles Marsh in 1878, is a neo-Latin term derived from Greek διπλός (diplos) "double" and δοκός (dokos) "beam",[3][5] in reference to the double-beamed chevron bones located in the underside of the tail, which were then considered unique.
This genus of dinosaurs lived in what is now mid-western North America at the end of the Jurassic period. Diplodocus is one of the more common dinosaur fossils found in the middle to upper Morrison Formation, between about 154 and 152 million years ago, during the late Kimmeridgian age.[6] The Morrison Formation records an environment and time dominated by gigantic sauropod dinosaurs, such s Apatosaurus, Barosaurus, Brachiosaurus, Brontosaurus, and Camarasaurus.[7] Its great size may have been a deterrent to the predators Allosaurus and Ceratosaurus: their remains have been found in the same strata, which suggests that they coexisted with Diplodocus.
Diplodocus is among the most easily identifiable dinosaurs, with its typical sauropod shape, long neck and tail, and four sturdy legs. For many years, it was the longest dinosaur known.
How is Diplodocus Different from Brontosaurus?
Diplodocus and Brontosaurus were closely related. Both were plant-eaters and they probably liked to eat the same types of plants. These long-necked dinosaurs lived in the Late Jurassic and their fossils have been found in the same country (United States of America). Diplodocus was different from Brontosaurus in a number of ways, Diplodocus had a much longer tail and its neck was longer and more slender than Brontosaurus. Brontosaurus was probably much heavier than Diplodocus.
What’s the raptor doing in that tractor?! In real life, Velociraptors would have probably been terrible farmers because they were carnivores and only ate meat! What meal would you offer a Velociraptor so it wouldn’t eat you?
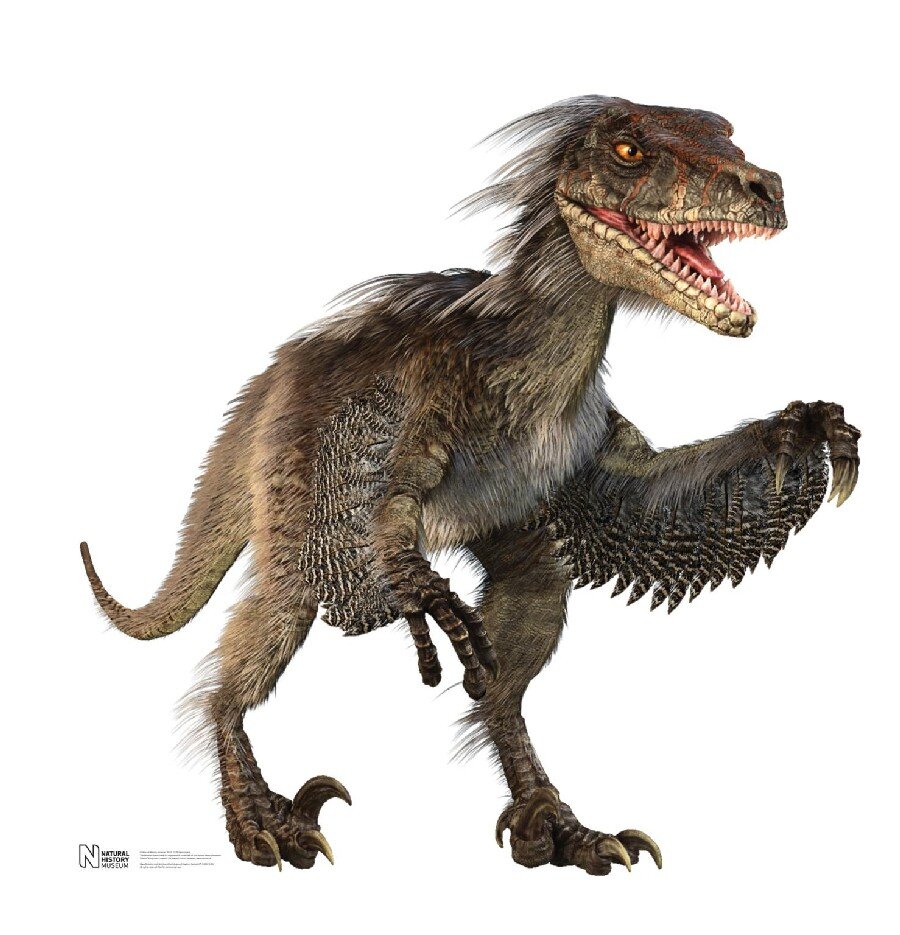
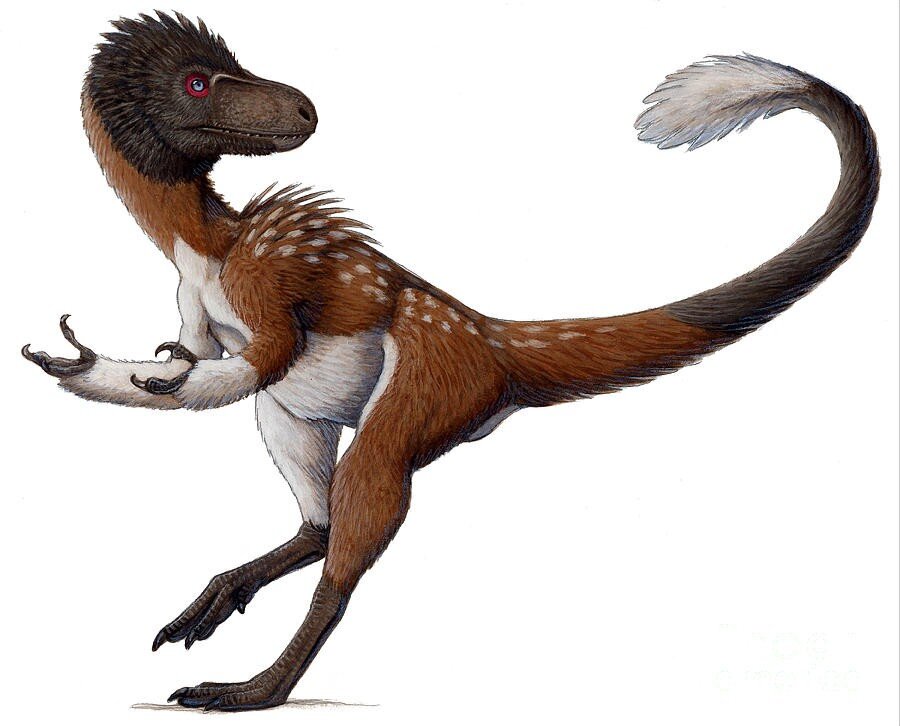
Velociraptor
Velociraptor "swift seizer" in Latin, is a genus of dromaeosaurid theropod dinosaur that lived approximately 75 to 71 million years ago during the latter part of the Cretaceous Period. Two species are currently recognized, although others have been assigned in the past. The type species is V. mongoliensis; fossils of this species have been discovered in Mongolia. A second species, V. osmolskae, was named in 2008 for skull material from Inner Mongolia, China.
Smaller than Deinonychus and Achillobator, Velociraptor nevertheless shared many of the same anatomical features. It was a bipedal, feathered carnivore with a long tail and an enlarged sickle-shaped claw on each hindfoot, which is thought to have been used to tackle and disembowel prey. Velociraptor can be distinguished from other dromaeosaurids by its long and low skull, with an upturned snout.
Velociraptor (commonly shortened to "raptor") is one of the dinosaur genera most familiar to the general public due to its prominent role in the Jurassic Park motion picture series. In real life, however, Velociraptor was roughly the size of a turkey, considerably smaller than the approximately 2 m (7 ft) tall and 80 kg (180 lb) reptiles seen in the films (which were based on members of the related genus Deinonychus). Today, Velociraptor is well known to paleontologists, with over a dozen described fossil skeletons, the most of any dromaeosaurid. One particularly famous specimen preserves a Velociraptor locked in combat with a Protoceratops.
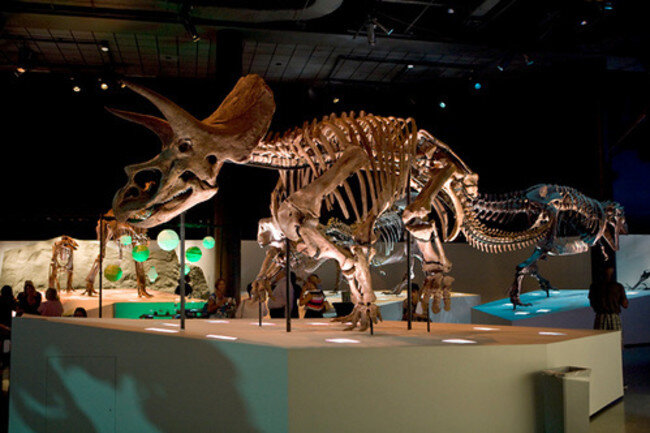
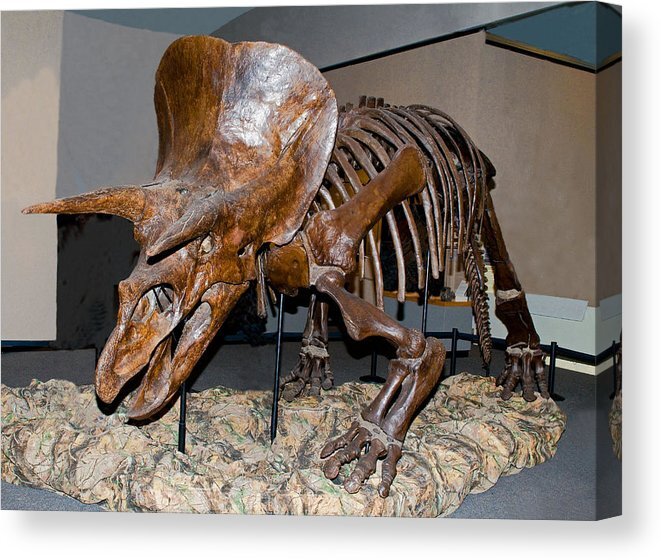
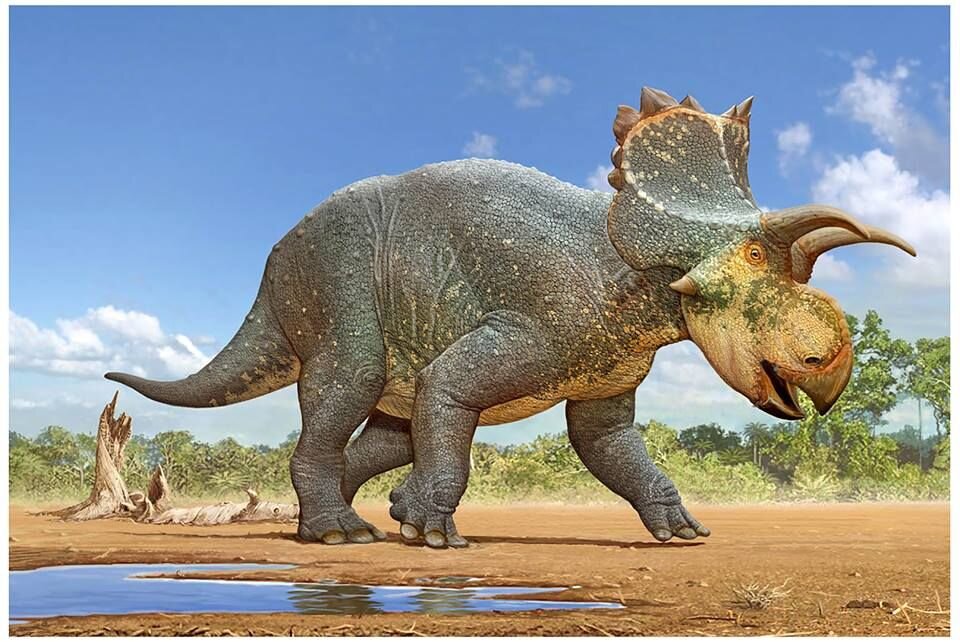
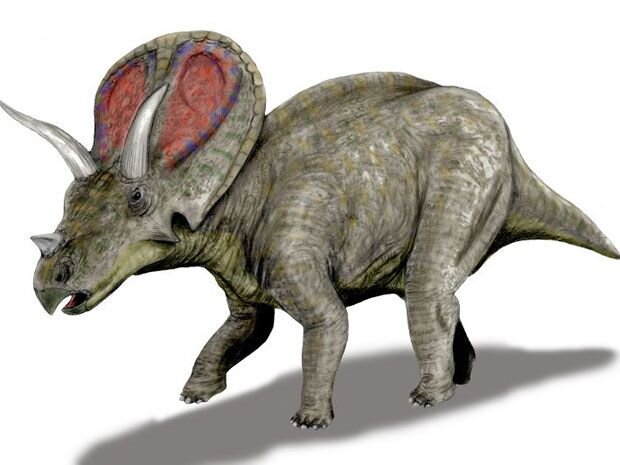
Triceratops
Triceratops is a genus of herbivorous ceratopsid dinosaur that first appeared during the late Maastrichtian stage of the late Cretaceous period, about 68 million years ago (mya) in what is now North America. It is one of the last known non-avian dinosaur genera, and became extinct in the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event 66 million years ago. The name Triceratops, which literally means "three-horned face", is derived from the Ancient Greek words τρί- (tri-) meaning "three", κέρας (kéras) meaning "horn", and ὤψ (ōps) meaning "face".
Triceratops has been documented by numerous remains collected since the genus was first described in 1889 by Othniel Charles Marsh. Specimens representing life stages from hatchling to adult have been found. As the archetypal ceratopsid, Triceratops is one of the most popular dinosaurs, and has been featured in film, postal stamps, and many other types of media.
Bearing a large bony frill and three horns on the skull, and its large four-legged body possessing similarities with the modern rhinoceros, Triceratops is one of the most recognizable of all dinosaurs and the best known ceratopsid. It was also one of the largest, up to nine metres long and twelve tonnes in weight. It shared the landscape with and was probably preyed upon by Tyrannosaurus, though it is less certain that the two did battle in the manner often depicted in museum displays and popular images. The functions of the frills and three distinctive facial horns on its head have long inspired debate. Traditionally, these have been viewed as defensive weapons against predators. More recent interpretations find it probable that these features were primarily used in species identification, courtship and dominance display, much like the antlers and horns of modern species.
Triceratops was traditionally placed within the "short-frilled" ceratopsids but modern cladistic studies show it to be a member of the Chasmosaurinae which usually have long frills. Two species, T. horridus and T. prorsus, are considered valid today, from the seventeen species that have ever been named. Research published in 2010 concluded that the contemporaneous Torosaurus, a ceratopsid long regarded as a separate genus, represents Triceratops in its mature form. This view was immediately disputed with examination of more fossil evidence needed to settle the debate.
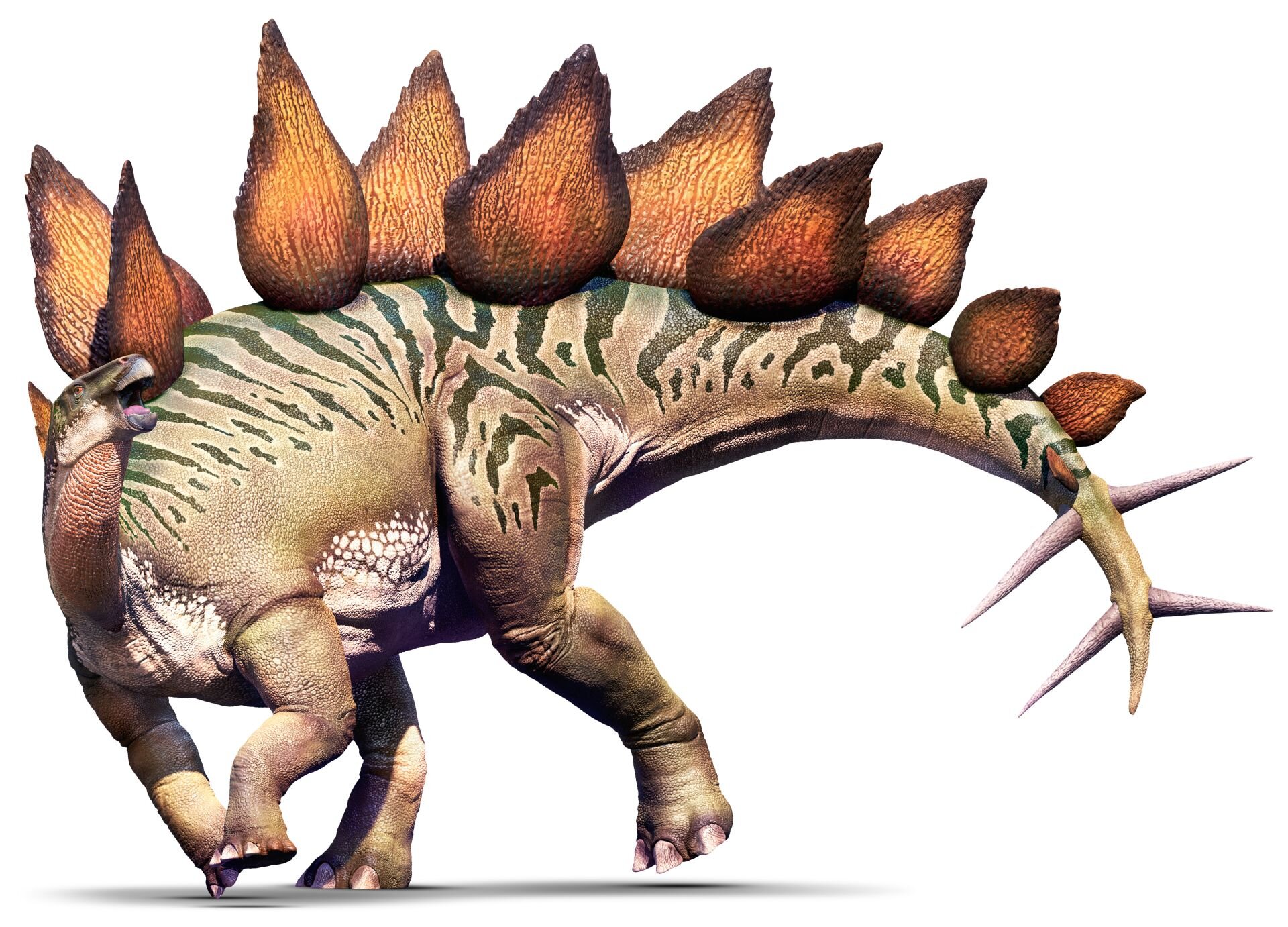
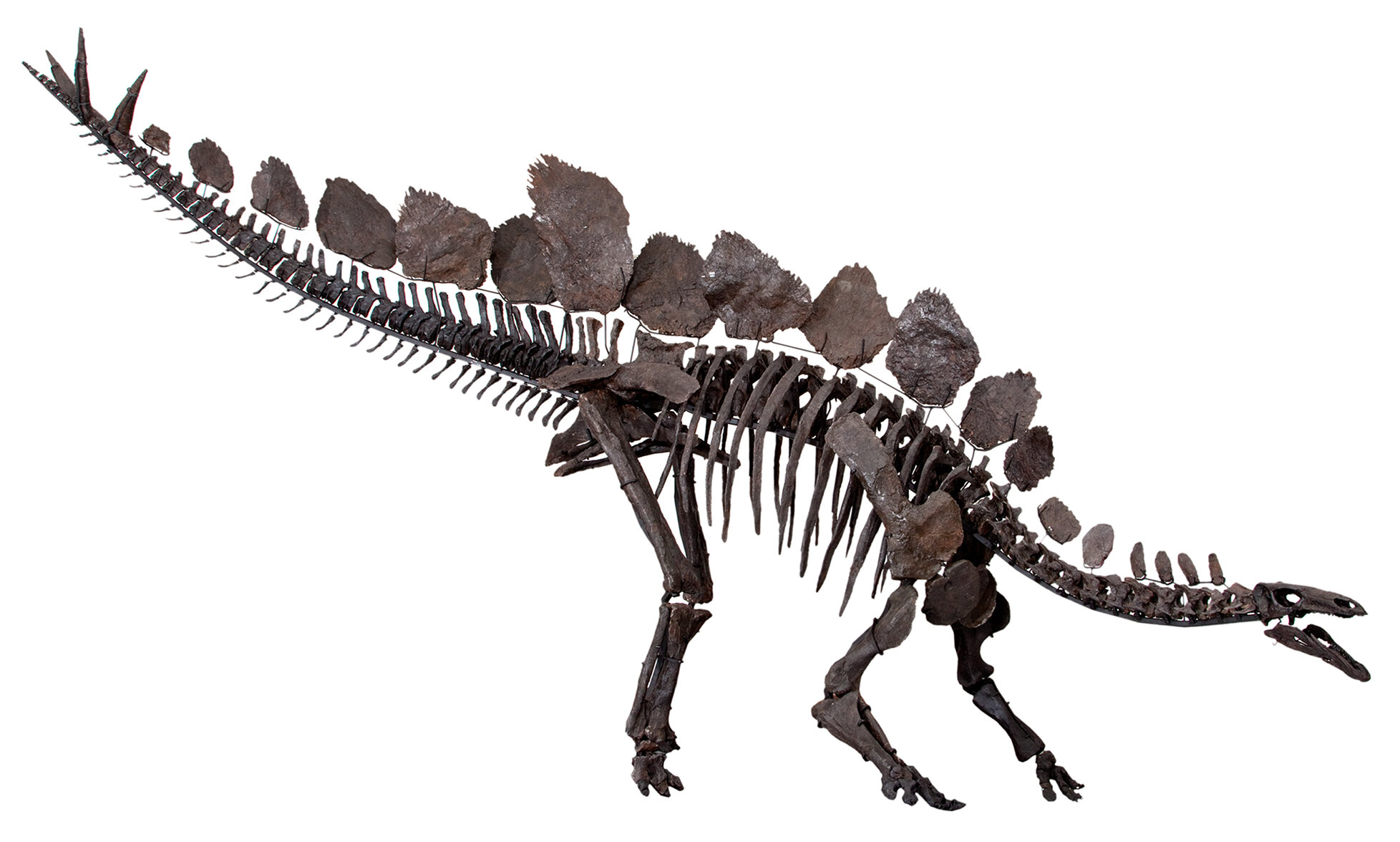
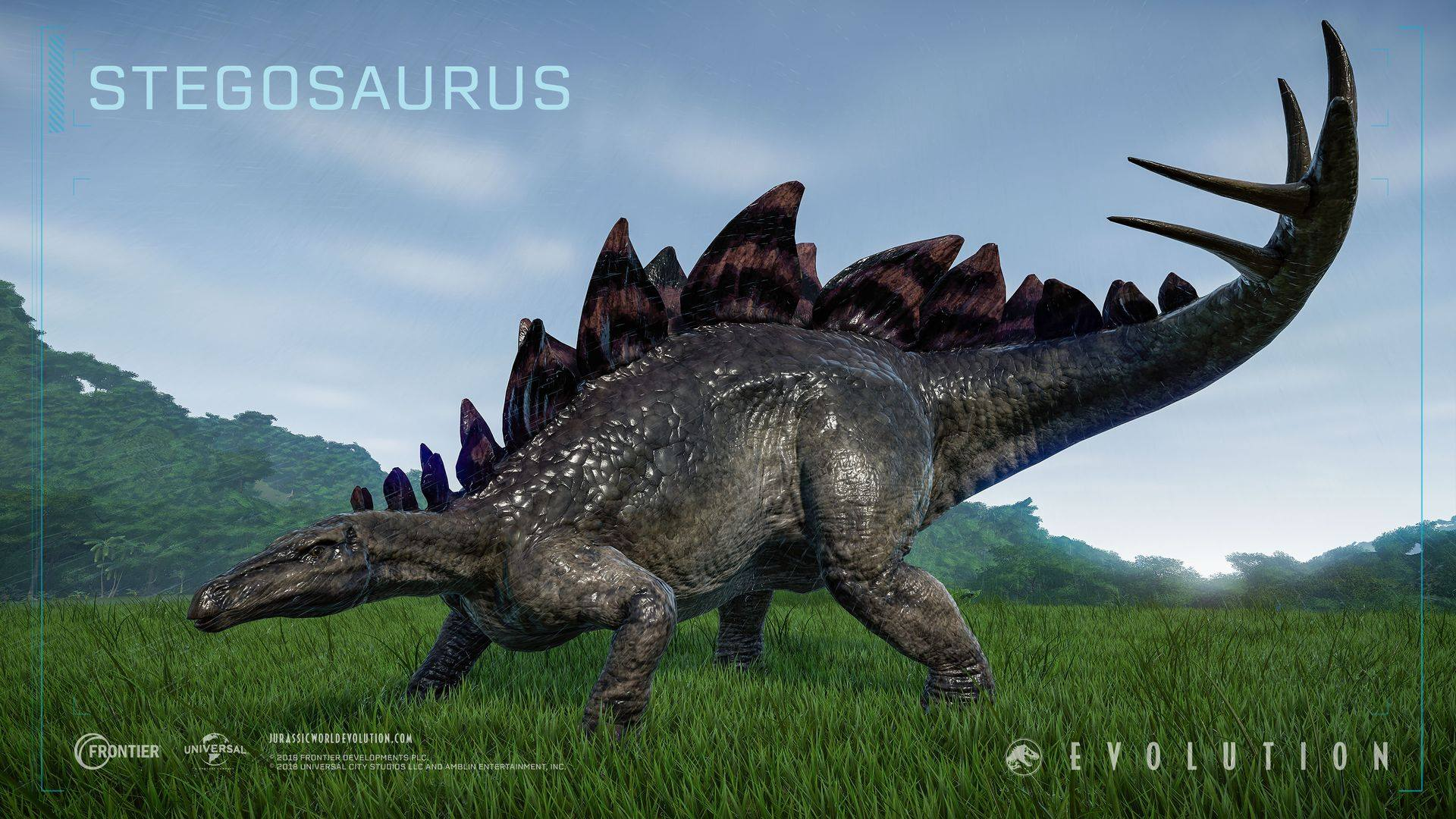
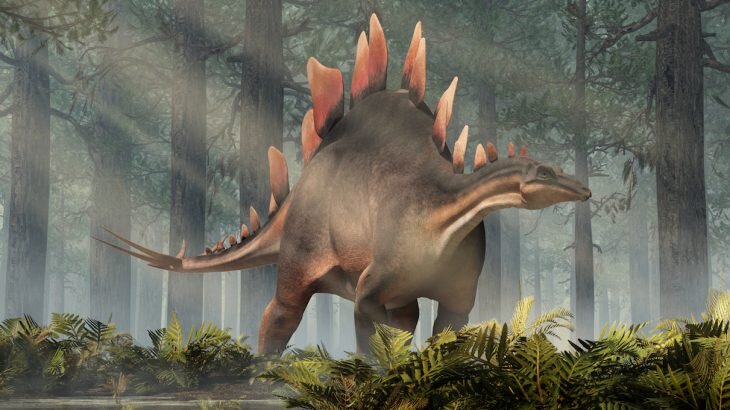
Stegosaurus
Stegosaurus from Greek stegos (στέγος) which means roof and sauros (σαῦρος) which means lizard, is a genus of herbivorous thyreophoran dinosaur. Fossils of this genus date to the Late Jurassic period, where they are found in Kimmeridgian to early Tithonian aged strata, between 155 and 150 million years ago, in the western United States and Portugal. Stegosaurus would have lived alongside dinosaurs such as Apatosaurus, Diplodocus, Brachiosaurus, Allosaurus, and Ceratosaurus; the latter two may have preyed on it.
These were large, heavily built, herbivorous quadrupeds with rounded backs, short fore limbs, long hind limbs, and tails held high in the air. Due to their distinctive combination of broad, upright plates and tail tipped with spikes, Stegosaurus is one of the most recognizable kinds of dinosaurs. The function of this array of plates and spikes has been the subject of much speculation among scientists. Today, it is generally agreed that their spiked tails were most likely used for defense against predators, while their plates may have been used primarily for display, and secondarily for thermoregulatory functions. Stegosaurus had a relatively low brain-to-body mass ratio. It had a short neck and a small head, meaning it most likely ate low-lying bushes and shrubs.
Stegosaurus remains were first identified during the "Bone Wars" by Othniel Charles Marsh at Dinosaur Ridge National Landmark. The first known skeletons were fragmentary and the bones were scattered, and it would be many years before the true appearance of these animals, including their posture and plate arrangement, became well understood. Despite its popularity in books and film, mounted skeletons of Stegosaurus did not become a staple of major natural history museums until the mid-20th century, and many museums have had to assemble composite displays from several different specimens due to a lack of complete skeletons. Stegosaurus is one of the best-known dinosaurs, and has been featured in film, postal stamps, and many other types of media.
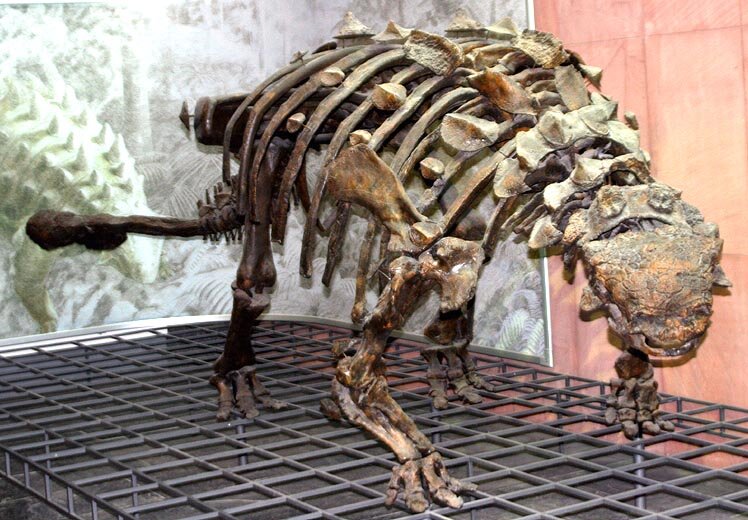
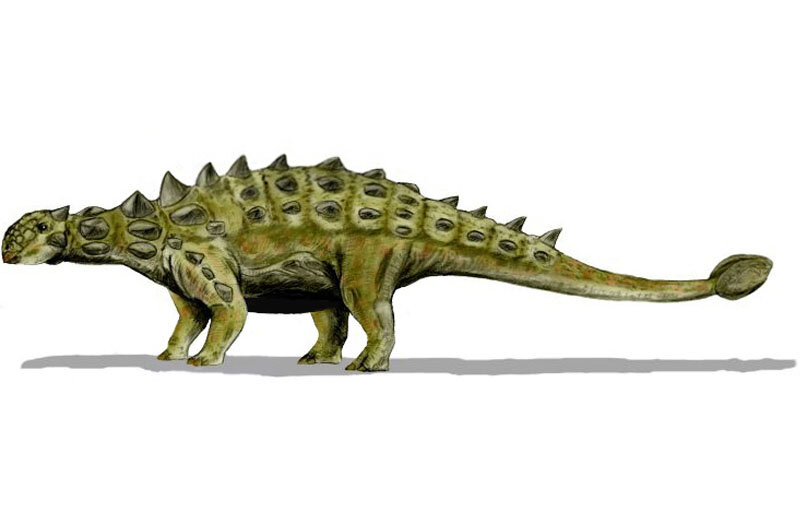
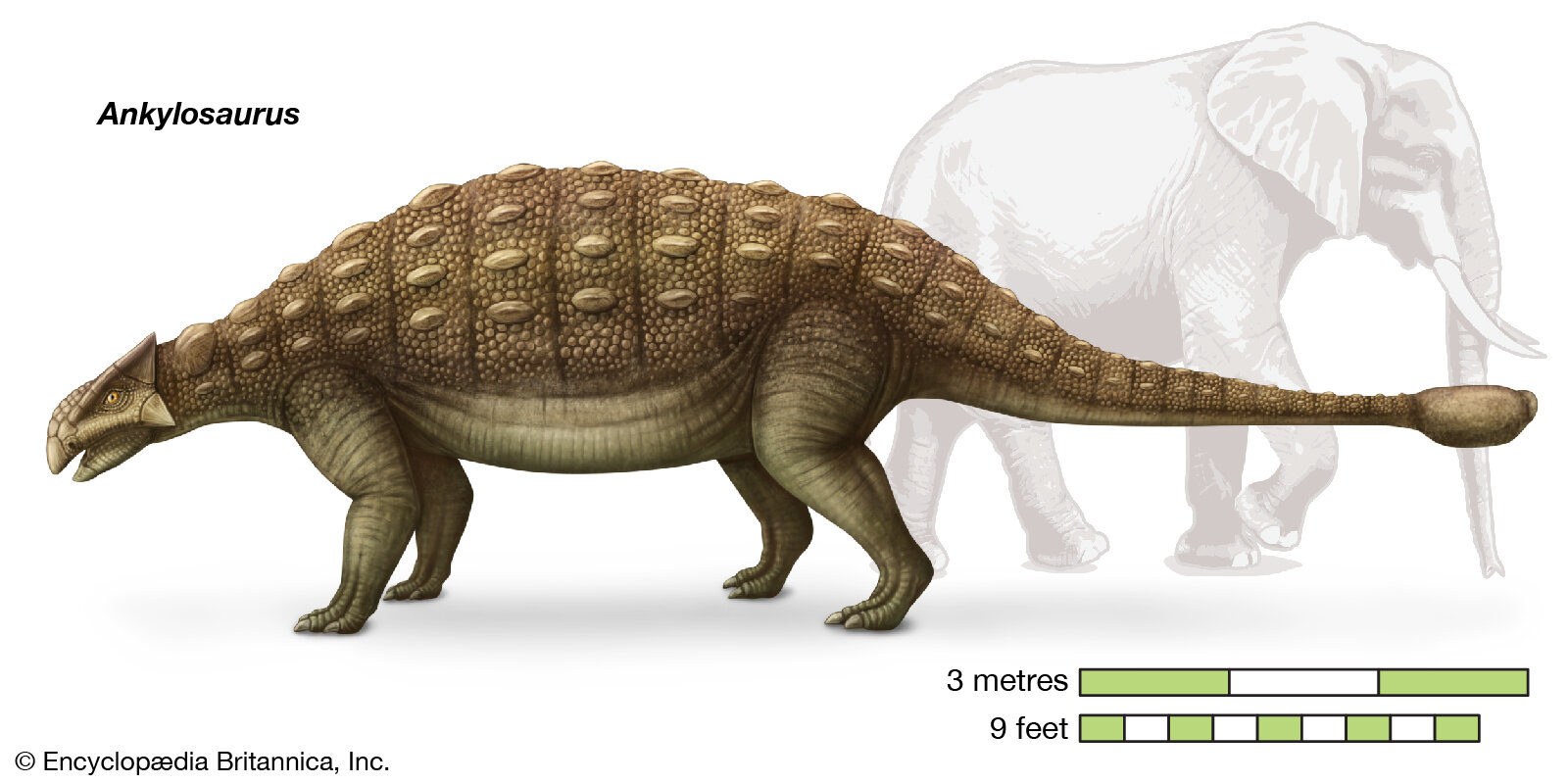
Ankylosaurus
Ankylosaurus is a genus of armored dinosaur. Its fossils have been found in geological formations dating to the very end of the Cretaceous Period, about 68–66 million years ago, in western North America, making it among the last of the non-avian dinosaurs. It was named by Barnum Brown in 1908. The genus name means "fused lizard", and the specific name means "great belly". A handful of specimens have been excavated to date, but a complete skeleton has not been discovered. Though other members of Ankylosauria are represented by more extensive fossil material, Ankylosaurus is often considered the archetypal member of its group, despite having some unusual features.
Possibly the largest-known ankylosaurid, Ankylosaurus is estimated to have been between 6 and 8 metres (20 and 26 ft) long and to have weighed between 4.8 and 8 tonnes (4.7 and 7.9 long tons). It was quadrupedal, with a broad, robust body. It had a wide, low skull, with two horns pointing backward from the back of the head, and two horns below these that pointed backward and down. Unlike other ankylosaurs, its nostrils faced sideways rather than towards the front. The front part of the jaws was covered in a beak, with rows of small, leaf-shaped teeth farther behind it. It was covered in armor plates, or osteoderms, with bony half-rings covering the neck, and had a large club on the end of its tail. Bones in the skull and other parts of the body were fused, increasing their strength, and this feature is the source of the genus name.
Ankylosaurus is thought to have been a slow-moving animal, able to make quick movements when necessary. Its broad muzzle indicates it was a non-selective browser. Sinuses and nasal chambers in the snout may have been for heat and water balance or may have played a role in vocalization. The tail club is thought to have been used in defense against predators or in intraspecific combat. Ankylosaurus has been found in the Hell Creek, Lance, Scollard, Frenchman, and Ferris formations, but appears to have been rare in its environment. Ankylosaurus also lived alongside dinosaurs such as Tyrannosaurus, Triceratops, and Edmontosaurus.
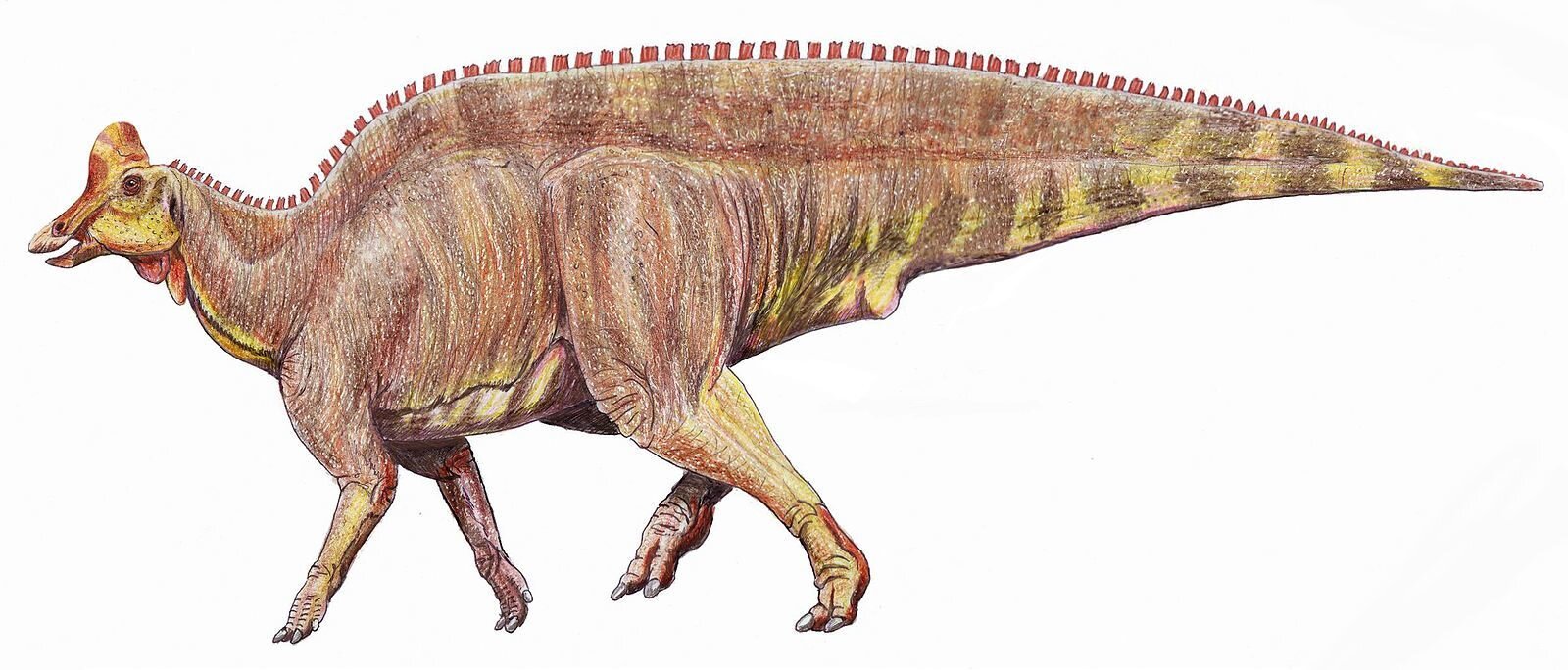
Hadrosaur
Hadrosaurids (Greek: ἁδρός, hadrós, "stout, thick"), or duck-billed dinosaurs, are members of the ornithischian family Hadrosauridae. This group is known as the duck-billed dinosaurs for the flat duck-bill appearance of the bones in their snouts. The family, which includes ornithopods such as Edmontosaurus and Parasaurolophus, was a common group of herbivores during the Late Cretaceous Period in what is now Asia, Europe, Antarctica, South America, and North America. Hadrosaurids are descendants of the Upper Jurassic/Lower Cretaceous iguanodontian dinosaurs and had a similar body layout.
Hadrosaurids were facultative bipeds, with the young of some species walking mostly on two legs and the adults walking mostly on four. Their jaws were evolved for grinding plants, with multiple rows of teeth replacing each other as the teeth wore down.
Hadrosaurids were the first dinosaur family to be identified in North America - the first traces being found in 1855-1856 with the discovery of fossil teeth.
Gallimimus
Gallimimus (GAL-i-MY-məs) is a genus of theropod dinosaur that lived in what is now Mongolia during the Late Cretaceous period, about seventy million years ago. Gallimimus is the largest known ornithomimid; adults were about 6 metres (20 ft) long, 1.9 metres (6 ft 3 in) tall at the hip and weighed about 440 kilograms (970 lb). As evidenced by its relative Ornithomimus, it would have had feathers. The head was small and light with large eyes that faced to the sides. The snout was long compared to other ornithomimids, although it was broader and more rounded at the tip than in other species. Gallimimus was toothless with a keratinous (horny) beak, and had a delicate lower jaw. Many of the vertebrae had openings that indicate they were pneumatic (air-filled). The neck was proportionally long in relation to the trunk. The hands were proportionally the shortest of any ornithomimosaur and each had three digits with curved claws. The forelimbs were weak while the hindlimbs were proportionally long.
Several fossils in various stages of growth were discovered by Polish-Mongolian expeditions in the Gobi Desert of Mongolia during the 1960s; a large skeleton discovered in this region was made the holotype specimen of the new genus and species Gallimimus bullatus in 1972. The generic name means "chicken mimic", referring to the similarities between its neck vertebrae and those of the Galliformes. At the time it was named, the fossils of Gallimimus represented the most complete and best preserved ornithomimid material yet discovered, and the genus remains one of the best known members of the group. The family Ornithomimidae is part of the group Ornithomimosauria, the "ostrich dinosaurs". Anserimimus, also from Mongolia, is thought to have been the closest relative of Gallimimus.
As an ornithomimid, Gallimimus would have been a fleet (or cursorial) animal, using its speed to escape predators; its speed has been estimated at 42–56 km/h (29–34 mph). It may have had good vision and intelligence comparable to ratite birds. Gallimimus may have lived in groups, based on the discovery of several specimens preserved in a bone bed. Various theories have been proposed regarding the diet of Gallimimus and other ornithomimids. The highly mobile neck may have helped locate small prey on the ground, but it may also have been an opportunistic omnivore. It has also been suggested that it used small columnar structures in its beak for filter-feeding in water, though these structures may instead have been ridges used for feeding on tough plant material, indicative of a herbivorous diet. Gallimimus is the most commonly found ornithomimosaur in the Nemegt Formation, where it lived alongside its relatives Anserimimus and Deinocheirus. Gallimimus was featured in the movie Jurassic Park, in a scene that was important to the history of special effects, and in shaping the common conception of dinosaurs as bird-like animals.
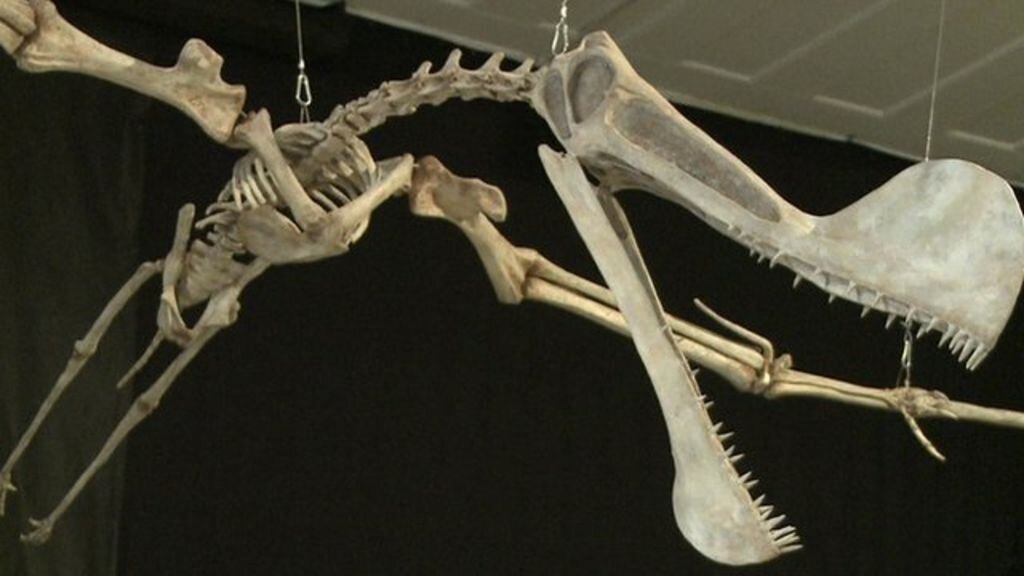
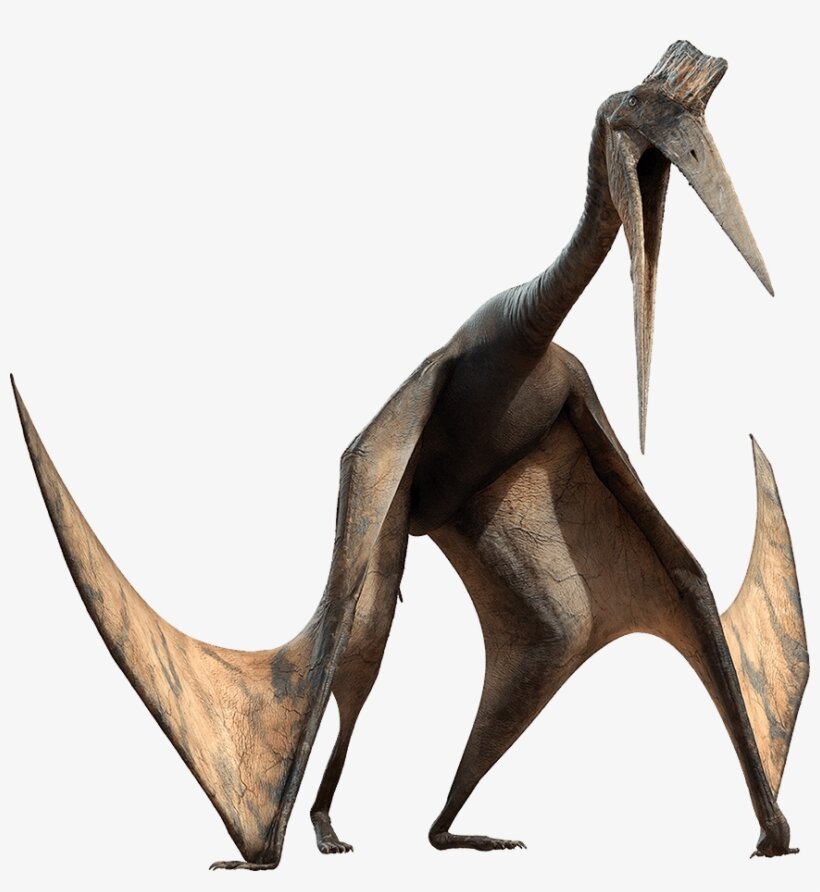
Pterosaur
Pterosaurs from Greek pteron and sauros, meaning "wing lizard") were flying reptiles of the extinct clade or order Pterosauria. They existed during most of the Mesozoic: from the late Triassic to the end of the Cretaceous (228 to 66 million years ago. Pterosaurs are the earliest vertebrates known to have evolved powered flight. Their wings were formed by a membrane of skin, muscle, and other tissues stretching from the ankles to a dramatically lengthened fourth finger.
Early species had long, fully toothed jaws and long tails, while later forms had a highly reduced tail, and some lacked teeth. Some, perhaps all, sported furry coats made up of hair-like filaments known as pycnofibers, which covered their bodies and parts of their wings. Some, perhaps all species, also had feathers, suggesting that feathers evolved in the common ancestor of pterosaurs and dinosaurs.The fur and feathers insulated their warm-blooded bodies. Their respiratory system used air sacs which hollowed out their bones to an extreme extent. Pterosaurs spanned a wide range of adult sizes, from the very small anurognathids to the largest known flying creatures of all time, including Quetzalcoatlus and Hatzegopteryx, which reached wingspans of at least nine metres. The combination of endothermy, a good oxygen supply and strong muscles allowed pterosaurs to be powerful and capable flyers.
Pterosaurs are often referred to by popular media or the general public as "flying dinosaurs", but dinosaurs are defined as the descendants of the last common ancestor of the Saurischia and Ornithischia, which excludes the pterosaurs.[11] Pterosaurs are nonetheless more closely related to birds and other dinosaurs than to crocodiles or any other living reptile, though they are not bird ancestors. Pterosaurs are also colloquially referred to as pterodactyls, particularly in fiction and by journalists. However, technically, pterodactyl only refers to members of the genus Pterodactylus, and more broadly to members of the suborder Pterodactyloidea of the pterosaurs.
Pterosaurs had a variety of lifestyles. Traditionally seen as fish-eaters, the group is now understood to have included hunters of land animals, insectivores, fruit eaters and even predators of other pterosaurs. They reproduced by means of eggs, some fossils of which have been discovered.
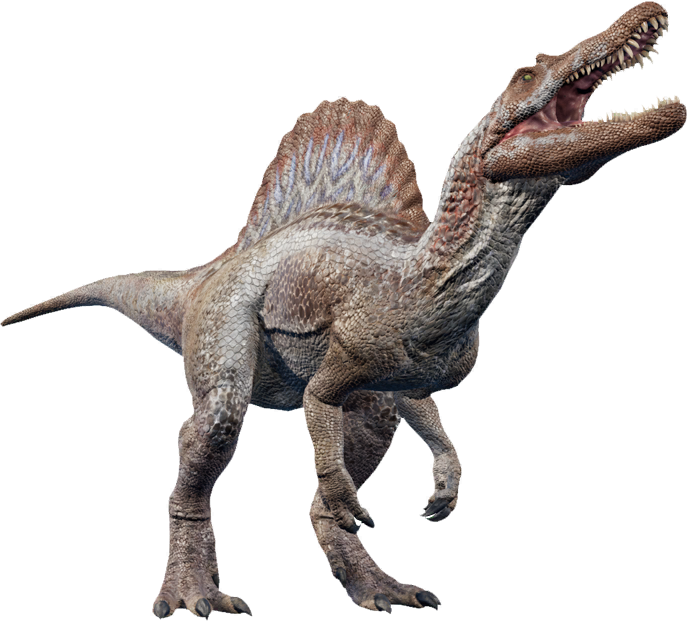
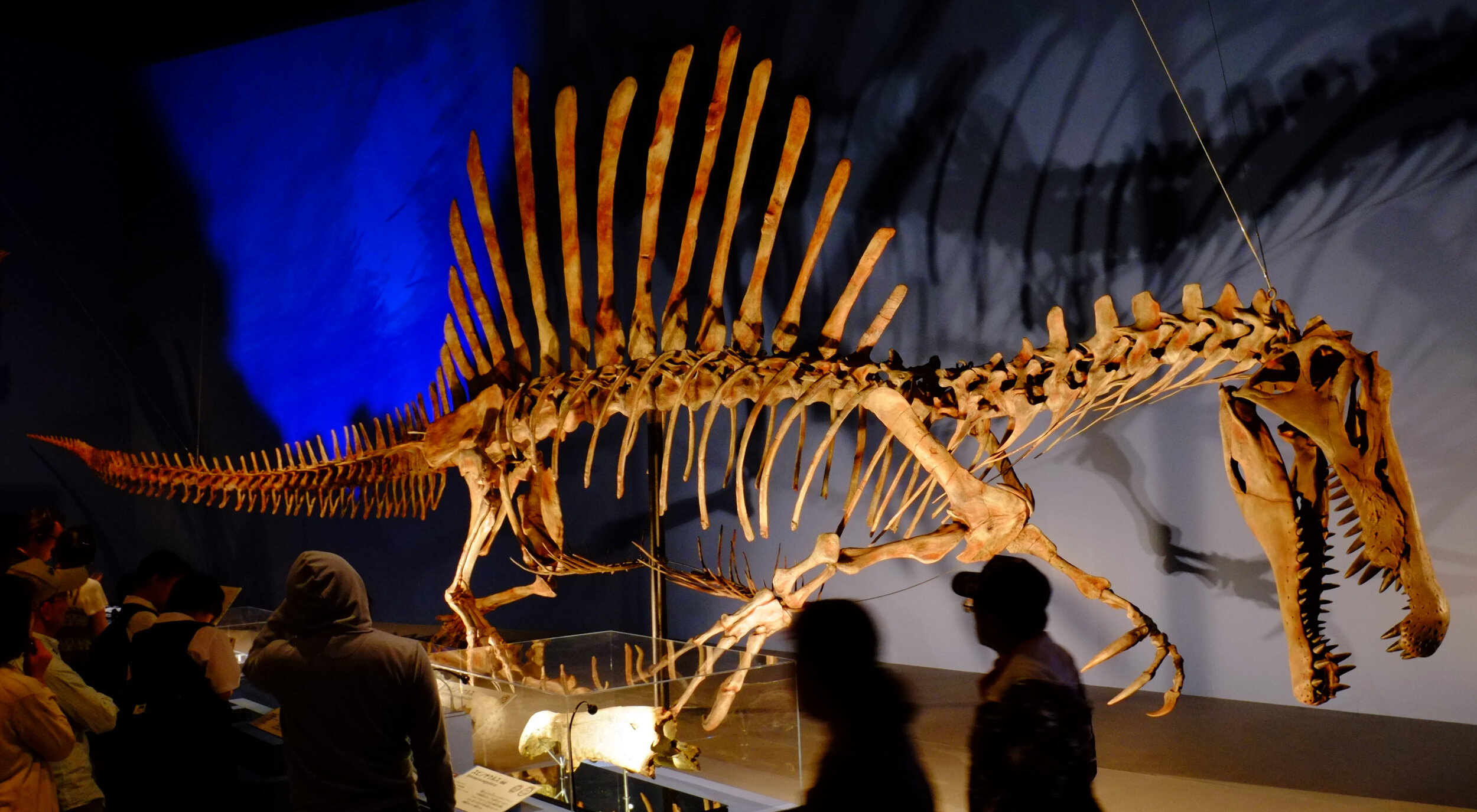
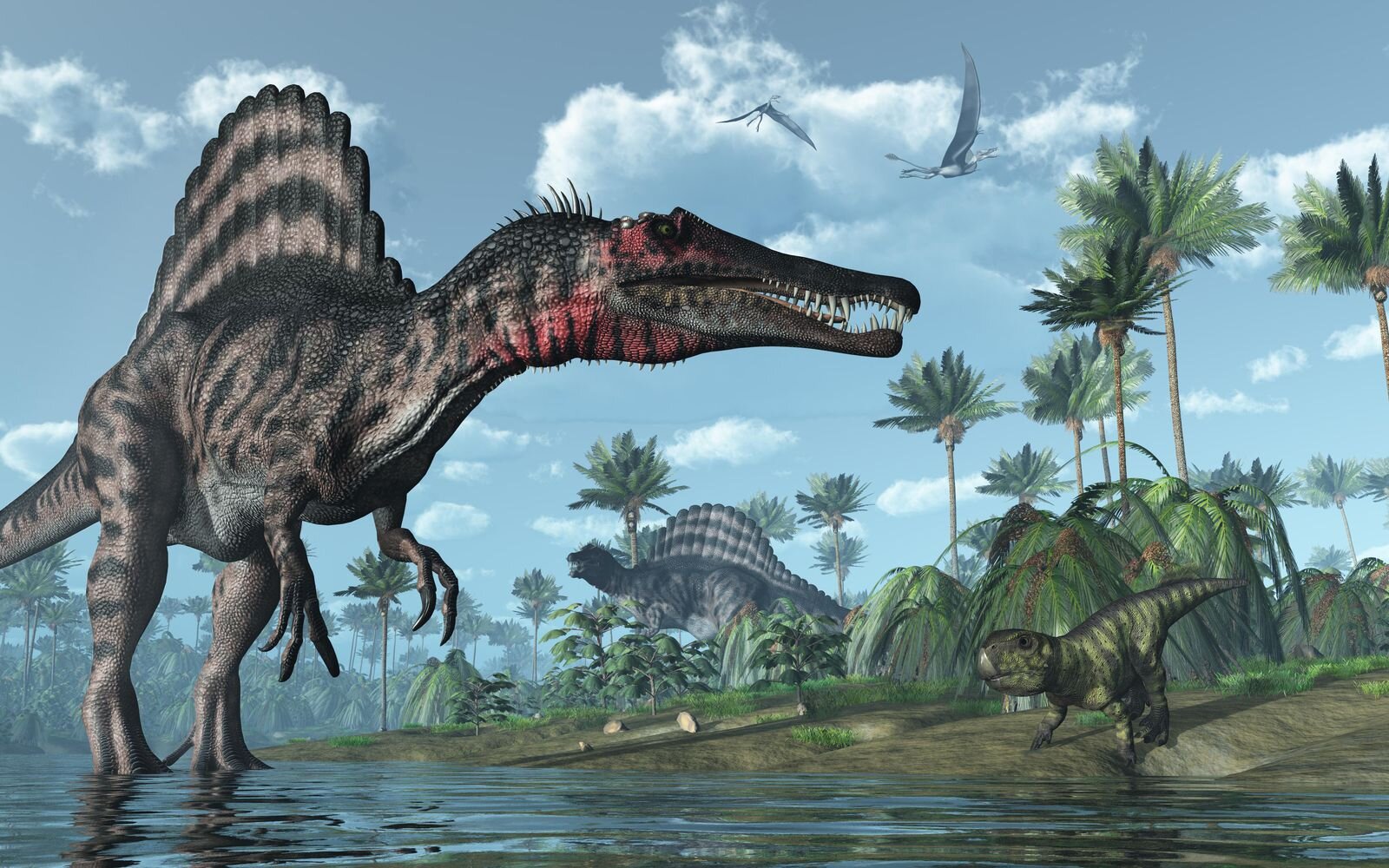
Spinosaurus
Spinosaurus (meaning "spine lizard") is a genus of theropod dinosaur that lived in what now is North Africa during the upper Albian to upper Turonian stages of the Cretaceous period, about 112 to 93.5 million years ago. This genus was known first from Egyptian remains discovered in 1912 and described by German paleontologist Ernst Stromer in 1915. The original remains were destroyed in World War II, but additional material has come to light in the early 21st century. It is unclear whether one or two species are represented in the fossils reported in the scientific literature.
Spinosaurus was among the largest of all known carnivorous dinosaurs, nearly as large as or even larger than Tyrannosaurus, Giganotosaurus and Carcharodontosaurus. Estimates published in 2005, 2007, and 2008 suggested that it was between 12.6–18 metres (41–59 ft) in length and 7 to 20.9 tonnes (7.7 to 23.0 short tons) in weight.New estimates published in 2014 and 2018, based on a more complete specimen, supported the earlier research, finding that Spinosaurus could reach lengths of 15–16 m (49–52 ft). The latest estimates suggest a weight of 6.4–7.5 tonnes (7.1–8.3 short tons). The skull of Spinosaurus was long and narrow, similar to that of a modern crocodilian. Spinosaurus is known to have eaten fish, and most scientists believe that it hunted both terrestrial and aquatic prey; evidence suggests that it lived both on land and in water as a modern crocodilian does. The distinctive spines of Spinosaurus, which were long extensions of the vertebrae, grew to at least 1.65 meters (5.4 ft) long and were likely to have had skin connecting them, forming a sail-like structure, although some authors have suggested that the spines were covered in fat and formed a hump. Multiple functions have been put forward for this structure, including thermoregulation and display.
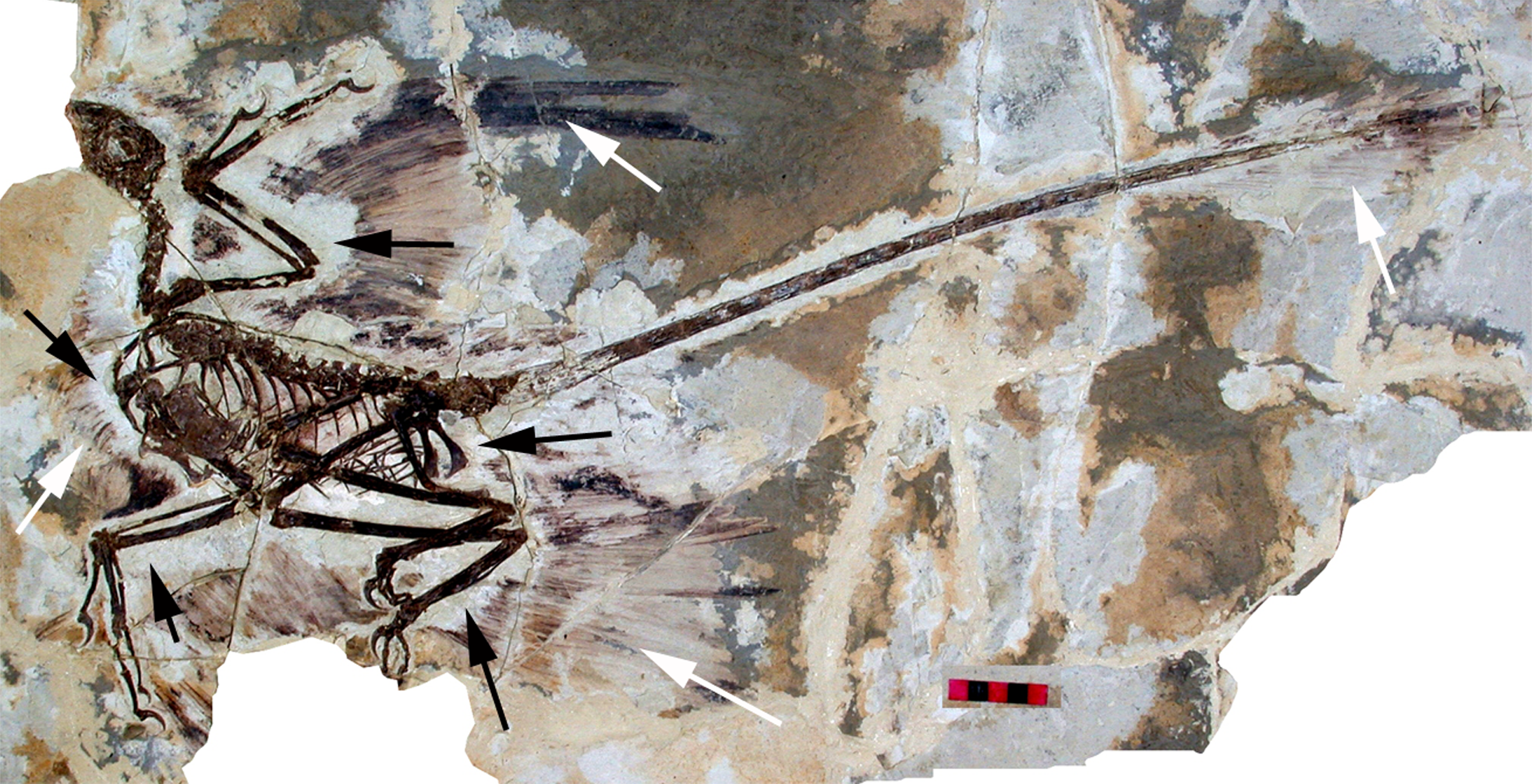
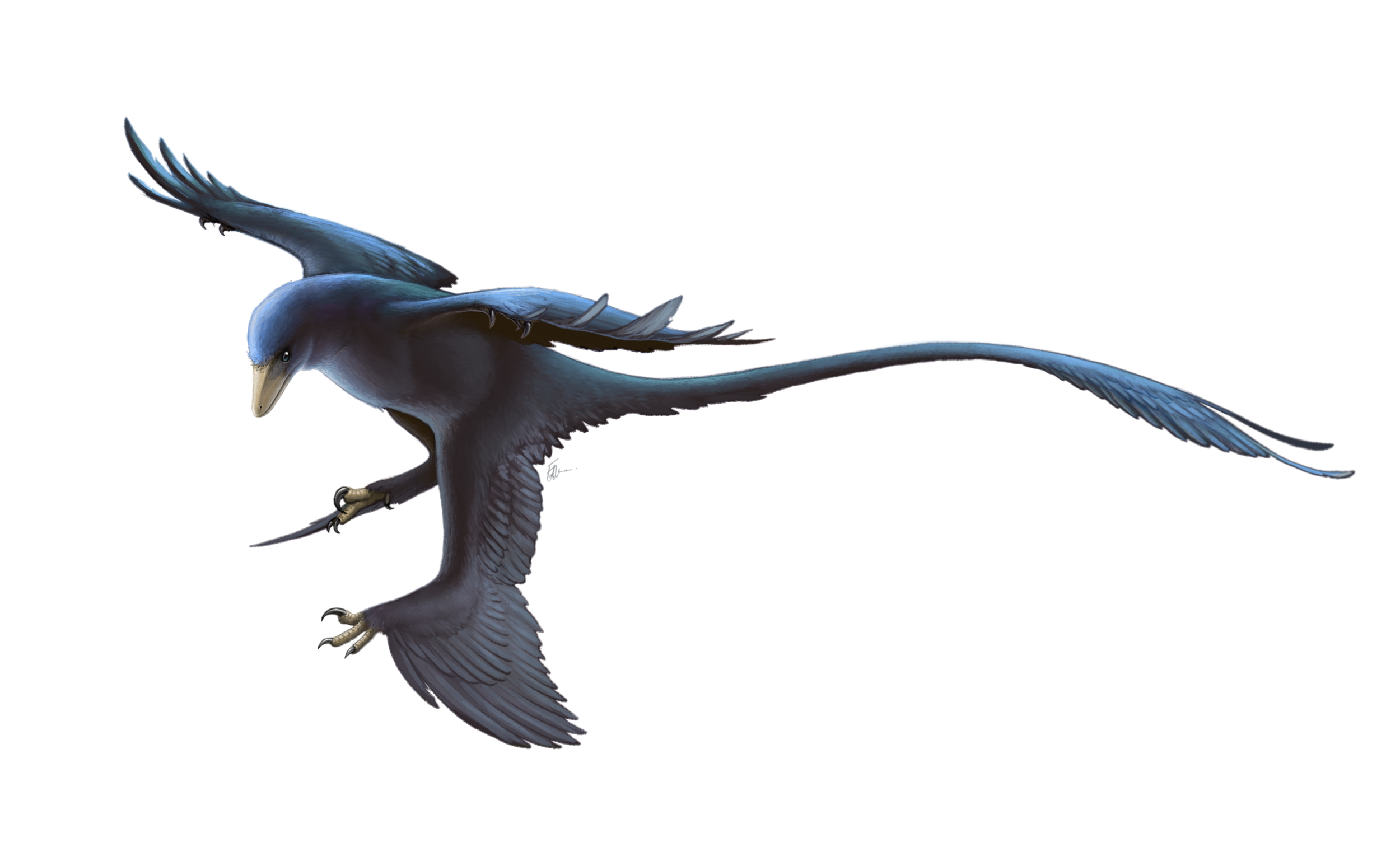
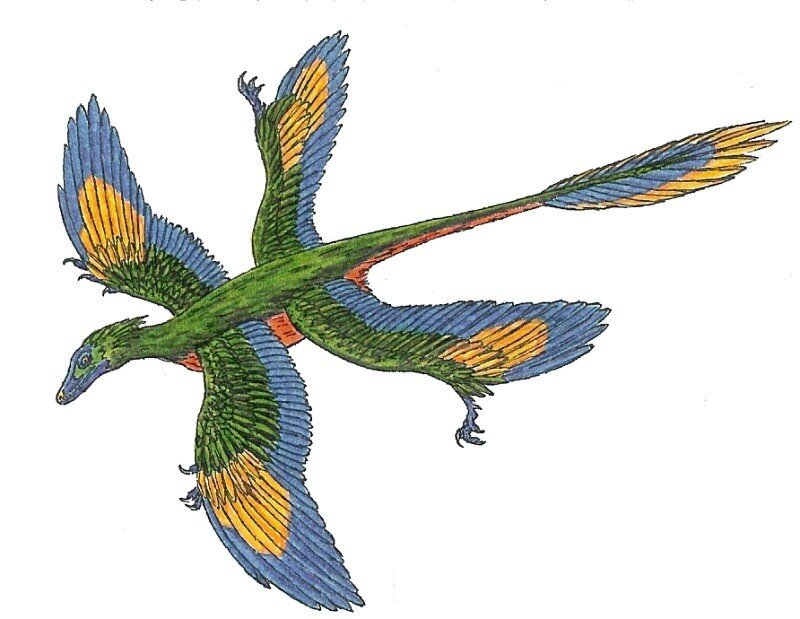
Microraptor
Microraptor (Greek, mīkros: "small"; Latin, raptor: "one who seizes") is a genus of small, four-winged paravian dinosaurs. Numerous well-preserved fossil specimens have been recovered from Liaoning, China. They date from the early Cretaceous Jiufotang Formation (Aptian stage), 120 million years ago.
Like Archaeopteryx, well-preserved fossils of Microraptor provide important evidence about the evolutionary relationship between birds and dinosaurs. Microraptor had long pennaceous feathers that formed aerodynamic surfaces on the arms and tail but also on the legs. This led paleontologist Xu Xing in 2003 to describe the first specimen to preserve this feature as a "four-winged dinosaur" and to speculate that it may have glided using all four limbs for lift. Subsequent studies have suggested that Microraptor was capable of powered flight as well.
Microraptor was among the most abundant non-avialan dinosaurs in its ecosystem, and the genus is represented by more fossils than any other dromaeosaurid, with possibly over 300 fossil specimens represented across various museum collections.
With adult specimens estimated up to 77 centimetres long (2.53 ft) and with a weight estimated up to 1 kilogram (2.2 lb), Microraptor was among the smallest-known non-avian dinosaurs. Microraptor were among the first non-avialan dinosaurs discovered with the impressions of feathers and wings. Microraptor is one of the few known bird precursors to sport long flight feathers on the legs as well as the wings. Their bodies had a thick covering of feathers, with a diamond-shaped fan on the end of the tail (possibly for added stability during flight).
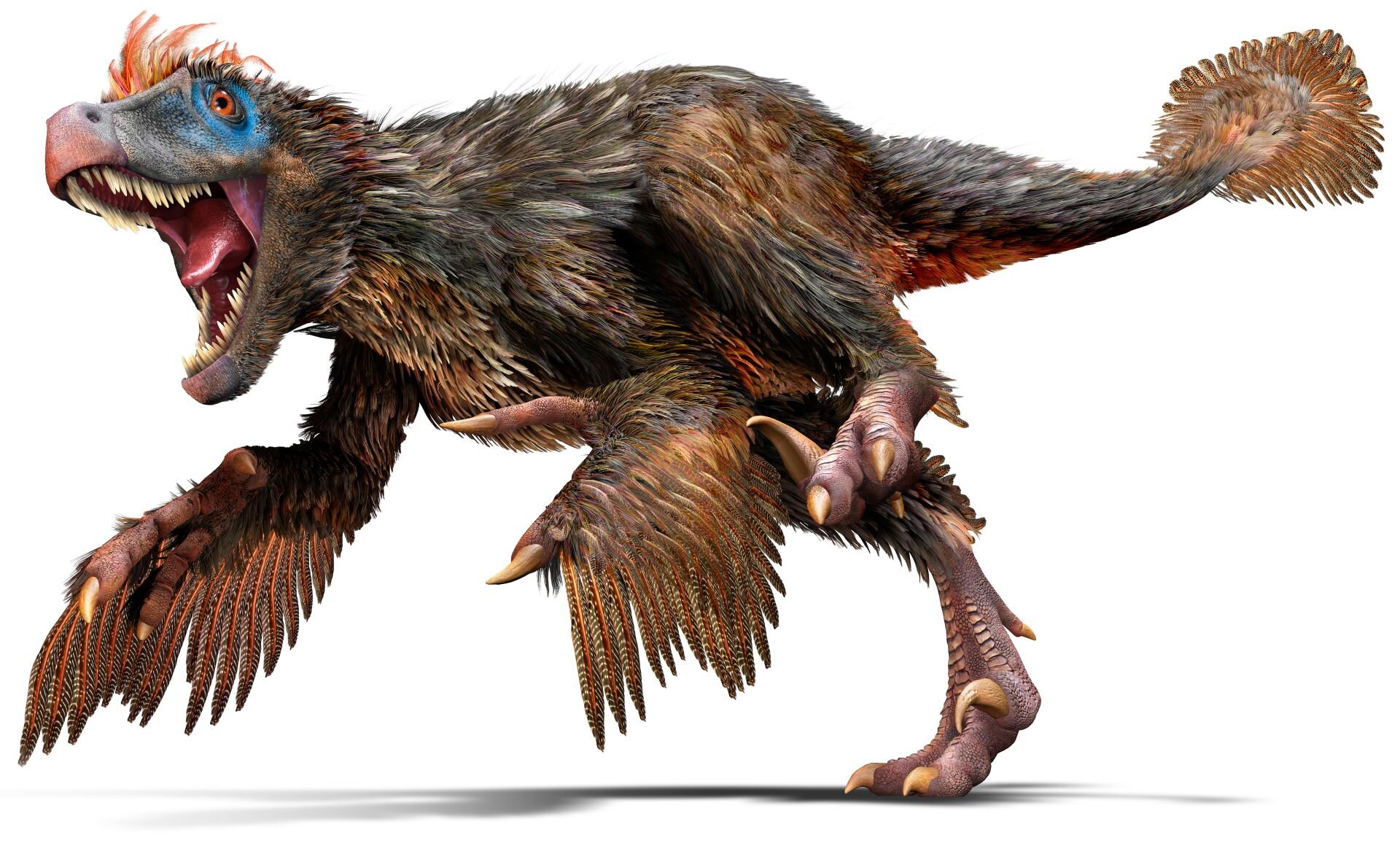
Dilong
Dilong (帝龍, which means 'emperor dragon') is a genus of basal tyrannosauroid dinosaur. The only species is Dilong paradoxus. It is from the Lower Cretaceous Yixian Formation near Lujiatun, Beipiao, the western Liaoning province of China. It lived about 126 million years ago.
Dilong was described by Xu Xing and colleagues in 2004. The name is derived from the Chinese 帝 dì meaning 'emperor' and 龙 / 龍 lóng meaning 'dragon'. "Di", "emperor", refers to the relationship of this animal to Tyrannosaurus rex, the "king" tyrannosaurid. "Long" is used to name Chinese dinosaurs in much the same way that the Latin -saur(us) is in the West. The specific name, paradoxus, is a Latinisation of the Ancient Greek παράδοξον meaning 'against received wisdom'.
Dilong paradoxus had a covering of simple feathers or protofeathers. The feathers were seen in fossilized skin impressions from near the jaw and tail. They are not identical to modern bird feathers, lacking a central shaft and most likely used for warmth, since they could not have enabled flight. Adult tyrannosaurs, found in Alberta and Mongolia have skin impressions which appear to show the pebbly scales typical of other dinosaurs. Xu et al. (2004) speculated that the tyrannosauroids may have had different skin coverings on different parts of their bodies—perhaps mixing scales and feathers. They also speculated that feathers may correlate negatively with body size—that juveniles may have been feathered, then shed the feathers and expressed only scales as the animal became larger and no longer needed insulation to stay warm.
When Dilong was first described, it was considered one of the earliest and most primitive members of Tyrannosauroidea, the group that includes the later, larger tyrannosaurids such as Tyrannosaurus rex. At least one later study, by Turner and colleagues in 2007, reanalyzed the relationships of coelurosaurian dinosaurs, including Dilong, and found that it was not a tyrannosauroid. Rather, they placed Dilong two steps above the tyrannosauroids in their phylogeny; more advanced than Coelurus, but more primitive than the Compsognathidae.[4] However, other studies continued to find Dilong as a tyrannosauroid, and some (such as Carr & Williamson 2010) found Dilong to fall within Tyrannosauroidea, not among the more advanced coelurosaurs.
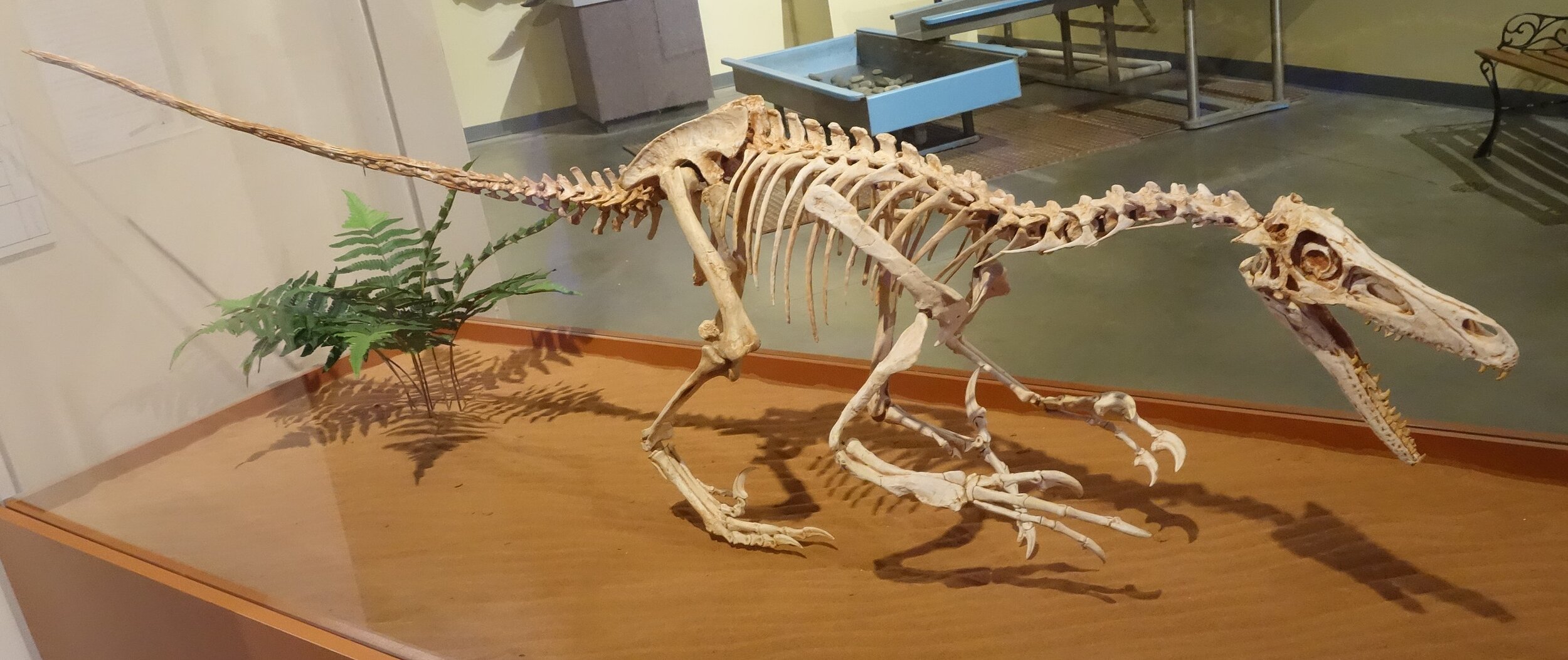
Iguanadon
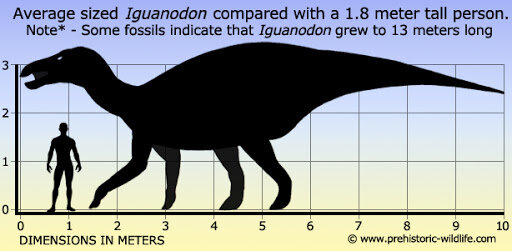
Iguanodon (meaning "iguana-tooth"), named in 1825, is a genus of ornithopod dinosaur that existed roughly halfway between the first of the swift bipedal hypsilophodontids of the mid-Jurassic and the duck-billed dinosaurs of the late Cretaceous. While many species have been classified in the genus Iguanodon, dating from the late Jurassic Period to the early Cretaceous Period of Asia, Europe, and North America, taxonomic revision in the early 21st century has defined Iguanodon to be based on one well-substantiated species: I. bernissartensis, which lived from the late Barremian to the earliest Aptian ages, Early Cretaceous) in Belgium, Spain, Germany, England and possibly elsewhere in Europe, between about 126 and 122 million years ago. Iguanodon were large, bulky herbivores. Distinctive features include large thumb spikes, which were possibly used for defense against predators, combined with long prehensile fifth fingers able to forage for food.
The genus was named in 1825 by English geologist Gideon Mantell but discovered by William Harding Bensted, based on fossil specimens found in England and was given the species name I. anglicus. Iguanodon was the second type of dinosaur formally named based on fossil specimens, after Megalosaurus. Together with Megalosaurus and Hylaeosaurus, it was one of the three genera originally used to define Dinosauria. The genus Iguanodon belongs to the larger group Iguanodontia, along with the duck-billed hadrosaurs. The taxonomy of this genus continues to be a topic of study as new species are named or long-standing ones reassigned to other genera. In 1878 new, far more complete remains of Iguanodon were discovered in Belgium and studied by Louis Dollo. These were given the new species I. bernissartensis.
Scientific understanding of Iguanodon has evolved over time as new information has been obtained from fossils. The numerous specimens of this genus, including nearly complete skeletons from two well-known bone beds, have allowed researchers to make informed hypotheses regarding many aspects of the living animal, including feeding, movement, and social behaviour. As one of the first scientifically well-known dinosaurs, Iguanodon has occupied a small but notable place in the public's perception of dinosaurs, its artistic representation changing significantly in response to new interpretations of its remains.
The discovery of Iguanodon has long been accompanied by a popular legend. The story goes that Gideon Mantell's wife, Mary Ann, discovered the first teeth of an Iguanodon in the strata of Tilgate Forest in Whitemans Green, Cuckfield, Sussex, England, in 1822 while her husband was visiting a patient. However, there is no evidence that Mantell took his wife with him while seeing patients. Furthermore, he admitted in 1851 that he himself had found the teeth, although he had previously stated in 1827 that Mrs. Mantell had indeed found the first of the teeth later named Iguanodon. Other later authors agree that the story is not certainly false. It is known from his notebooks that Mantell first acquired large fossil bones from the quarry at Whitemans Green in 1820. Because also theropod teeth were found, thus belonging to carnivores, he at first interpreted these bones, which he tried to combine into a partial skeleton, as those of a giant crocodile. In 1821 Mantell mentioned the find of herbivorous teeth and began to consider the possibility that a large herbivorous reptile was present in the strata. However, in his 1822 publication Fossils of the South Downs he as yet did not dare to suggest a connection between the teeth and his very incomplete skeleton, presuming that his finds presented two large forms, one carnivorous ("an animal of the Lizard Tribe of enormous magnitude"), the other herbivorous.
The largest find of Iguanodon remains to that date occurred on 28 February 1878 in a coal mine at Bernissart in Belgium, at a depth of 322 m (1,056 ft), when two mineworkers, Jules Créteur and Alphonse Blanchard, accidentally hit on a skeleton that they initially took for petrified wood. With the encouragement of Alphonse Briart, supervisor of mines at nearby Morlanwelz, Louis de Pauw on 15 May 1878 started to excavate the skeletons and in 1882 Louis Dollo reconstructed them. At least 38 Iguanodon individuals were uncovered, most of which were adults. In 1882, the holotype specimen of I. bernissartensis became one of the first ever dinosaur skeletons mounted for display. It was put together in a chapel at the Palace of Charles of Lorraine using a series of adjustable ropes attached to scaffolding so that a lifelike pose could be achieved during the mounting process. This specimen, along with several others, first opened for public viewing in an inner courtyard of the palace in July 1883. In 1891 they were moved to the Royal Museum of Natural History, where they are still on display; nine are displayed as standing mounts, and nineteen more are still in the Museum's basement. The exhibit makes an impressive display in the Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences, in Brussels. A replica of one of these is on display at the Oxford University Museum of Natural History and at the Sedgwick Museum in Cambridge. Most of the remains were referred to a new species, I. bernissartensis, a larger and much more robust animal than the English remains had yet revealed. The skeletons were some of the first complete dinosaur skeletons known.




























































Race time! Did you know you can get signed and personalized books at www.WhimsicalWorldBooks.com! Turn an everyday gift into a lifelong treasure.